Azure Management
Azure Management and Governance is hard because Azure services are growing at a fast pace. Try to imagine that you are a Azure Administrator for a large company and that you need to maintain the Azure Subscription.
If you start thinking about it sounds really hard and that makes you wonder about options that you have to manage and keep it running as it should be.
For managing your Azure environment there are a couple of capabilities. Ad the time of writing there are the following build-in options:
- Azure Policy & Audit
- Role Based Access Control
- Azure Automation
- Resource Locks
- Azure Security Center
- Resource Groups
- Azure Advisor
Role Based Access Control is a huge one here. This was in place since the beginning of the new Azure Portal. This made sure you did not have to make someone Co-Administrator on your complete subscription. Besides the build-in options there is also a need to define a policy regarding your Azure Environment also called a Governance document. In the document you need to specify naming conventions that are used for creating and naming of services. The options described above can help you maintain that Governance.
Azure Policy & Audit
Azure Policies and Audits help you manage risks within your Azure Environment / Subscription. Therefore it will help you by restricting, enforcing or auditing events.
Some key facts for policies and audits in Azure are:
- It is a default allow system. By default everything is allowed. You will need to define deny or audit actions.
- Policies are created by Policy definitions, which are if-then conditions.
- Policy definitions are defined in JSON
- Deployed and Maintained via the Resource Manager.
Policies within Azure can be build on three types of actions:
- Deny: Stop / Cancel the request.
- Audit: Add a specific message to the Audit log.
- Append: Add information to the resource. For example add a specific tag.
The defined policies can be enforced within the following scopes:
- Subscription
- Resource group
- Resource type
My article about Azure Policies published a few weeks ago shares some more information and also contains information about the implementation:
Besides the article I also maintain a GitHub repository with policies I created:
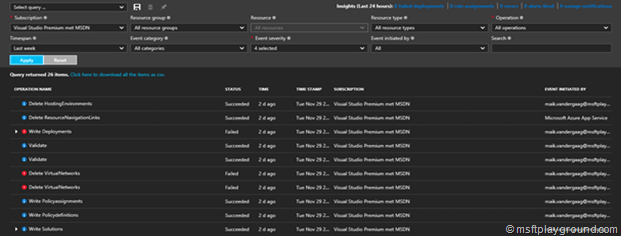
Alongside the policies you also have the activity (audit) log that gives insight in all activities in and around Azure.
Resource Locks
Resource locks support another type of management on your resources. With resource locks you for example are able to make a resource read-only. Which makes it possible to secure resources in another way. At the time of writing this article Resource Locks support two actions:
- CanNotDelete: You will not be able to delete the resources with this lock applied.
- ReadOnly: You only be able to read the resources with this lock applied, and will not be able to edit specific properties.
With a Resource Lock applied you can make sure someone does not accidentally delete a business critical application, or for example the virtual network with the connection to the on-premise systems.
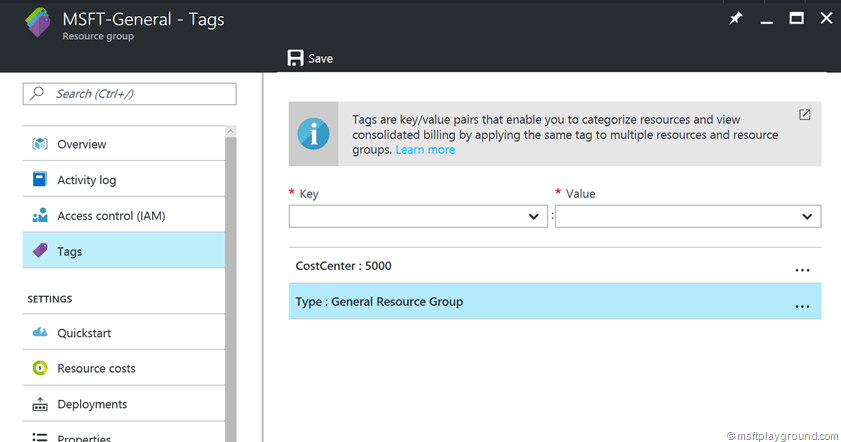
Resource Tags
Within Azure you have the option to add metadata to your resources in the form of tags. Tags are key value pairs that enable you to group and aggregate resources in various ways. With the use of Azure Policies you can also make sure that resources are tagged automatically with for example the Cost Center. Examples for tags are:
- Cost Center
- Department
- Owner
- Project
In my opinion you should always tag your resources groups with useful information and tag the resources within with the tags that are appropriate.
Resource Groups
A Resource group is a logical container for resources. You can resources by project or application for example.
The resource group gives you the ability to manage the following:
- Delete resources at once.
- Move resources at once.
- Assign rights for the resource group.
Because of the new model of Azure you can also assign rights within a Resource Group like Role-based access control to give access to resources.
Azure Automation
This service provides a way for people to automate the manual, long-running, error-prone, and frequently repeated tasks that are commonly performed in a enterprise environment.
With Azure Automation you create so called Runbooks that are sets of tasks that are needed to be performed. You can use Runbooks created by the community within you Azure Environment.
- Azure Automation: Script resources for IT professionals
- Runbook and module galleries for Azure Automation
Examples for Runbooks are:
- Automatically shut down Azure VM’s
- Start and run specific services.
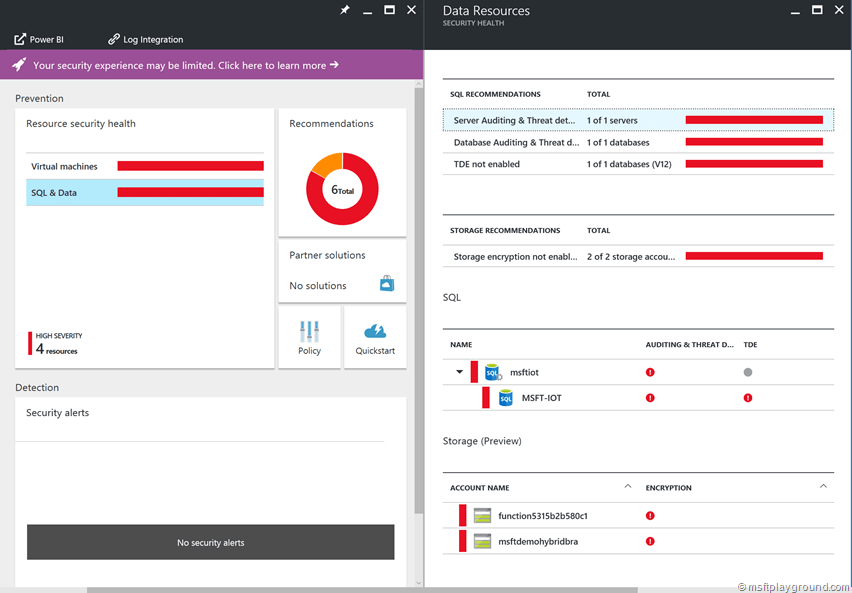
Azure Security Center
As Microsoft states Security Center helps you prevent, detect, and respond to threats with increased visibility into and control over the security of your Azure resources. It provides integrated security monitoring and policy management across your Azure subscriptions, helps detect threats that might otherwise go unnoticed, and works with a broad ecosystem of security solutions.
In the most simple form Azure Security Center is a service that gives you recommendation about the security of your services. Besides that it is also able to monitor the services in order to detect threats within your environment.
Policies within Security center can be turned off when they are not seen as threats and based on specific settings you can also define alerts.
Azure Advisor
Since last month “Azure Advisor” made it to public preview. The service is a recommendation engine that recommends steps to optimally configure your Azure resources. By analyzing the resource configuration and usage data it is able to make recommendations according to the best practices that in the long run will reduce costs and better the performance.
The Azure Advisor will give recommendation on four categories:
- High Availability
- Security
- Performance
- Costs
You may noticed that the list also contains a Security category this category is a integration with Azure Security Center.
For information and how to start using the service read the following article:
Useful links
- Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints
- Recommended naming conventions for Azure resources
- Use Policy to manage resources and control access
- Audit operations with Resource Manager
- Using tags to organize your Azure resources
- Lock resources with Azure Resource Manager
- Azure Automation overview
- Runbook and module galleries for Azure Automation
- Introduction to Azure Security Center
- Introduction to Azure Advisor