Control over a Azure Cloud environment? Create a governance plan!
Control over your cloud environment is great. In order to properly monitor and manage a cloud environment, it is important to draw up a cloud governance plan based on the company policy.
In this plan, you name all aspects that are essential and then implement the policy. But what steps do you need to take to draw up a good cloud governance plan?
For every organization it is important to keep control on the cloud environment. This is not only related to; who has rights where, it is also about making the costs transparent. If these costs are transparent, it is easy to make a so-called IT charge or showback of these costs.
IT chargeback and IT showback are two policies used by IT departments to inform and / or bill the costs for the use of each department of division. Read more about IT charge and showback here.
To get control over the cloud platform one of the first steps is write a cloud governance plan.
Cloud Governance
From the company policy the Cloud governance is formalized For this document, the following aspects are mainly considered:
- Business risks: Identifying and understanding business risks.
- Policy and compliance: Convert risk into statements that support any compliance requirements.
- Processes: Ensuring compliance with the established policy.
You then write up five disciplines based on this policy, which are:
- Cost management: Evaluate and monitor costs, keep IT expenses under control and gain insight into costs.
- Basic security: Ensure compliance with IT security requirements by applying a basic security line.
- Resource consistency: Provide consistency in resource configuration.
- Basic Identity Configuration: Ensure that the basis for identity and access is maintained by applying consistent role definitions and assignments.
- Deployment acceleration: Accelerate deployment through centralization, consistency, and standardization across resource templates.
Governance Implementation
After setting up the cloud governance, it is time for implementation. With the implementation you ensure that the established policy can be complied with and checked.
By applying cloud governance you ensure a cloud platform that is in the best possible status and that the platform is compliant. Within Azure there are various services that support you in setting up cloud governance. Check out this website for more information on Azure Governance.
Management groups
Management groups are virtual containers in which subscriptions are placed. By means of these containers the subscriptions can be placed in a hierarchy. This makes it possible to manage subscriptions uniformly and manage policies and access rights across multiple subscriptions.
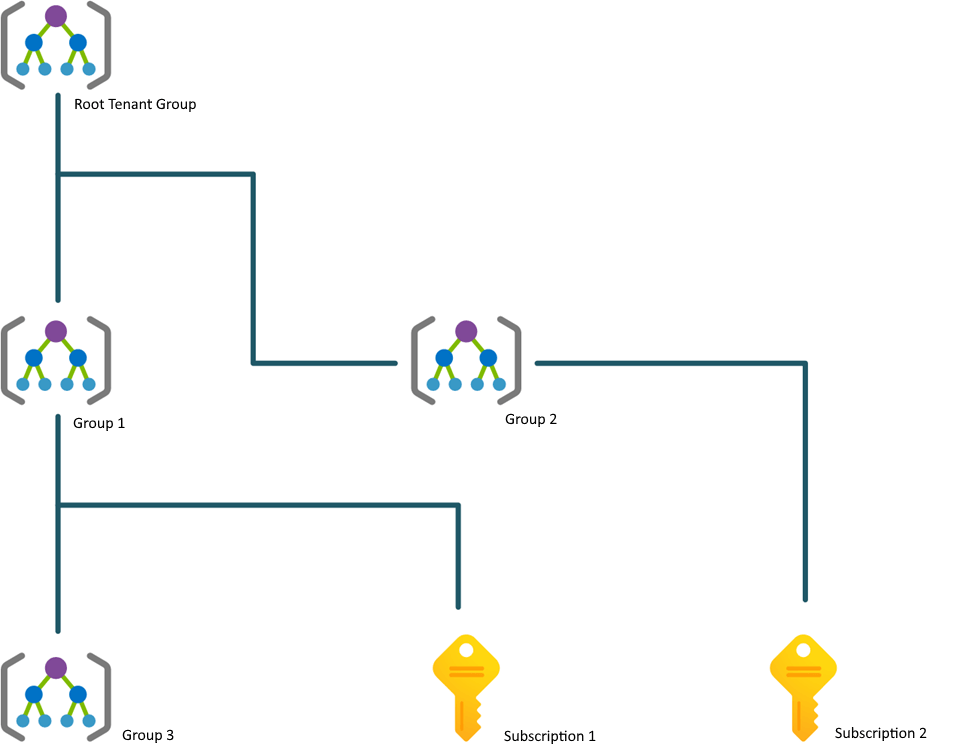
Some important points of Management groups are:
- A structure for Management groups is set up per Azure Active Directory;
- By default, a Tenant Root Management group is present per tenant.
Limits of Management groups are:
- One Azure Active Directory tenant can contain 10,000 management groups;
- The structure can be made up to 6 levels deep (excluding the Tenant Root Management group.);
- Groups or subscriptions can be placed in one group.
Azure Policies
As described, policies have been written down for the cloud platform. These policies can be enforced or registered through Azure Policies.
Azure Policies specifies the rules in a JSON format, making the rules easy to check by the platform. The platform itself has a large number of rules build-in, some examples for this are:
- Require tag and its value on resource groups;
- Allowed locations;
- A maximum of 3 owners should be designated for your subscription;
- MFA should be enabled on accounts with owner permissions on your subscription.
The above rules are a small selection of the policies that can be used by default. Next to that you can also specify customer policies to be compliant with your governance design.
Other Azure Services
In addition to Azure Policies and management groups, there are a large number of other Azure Services and platform functionalities that support cloud governance:
- Azure Automation: Automating various cloud infrastructure tasks.
- Azure Monitor: Monitoring resources and supporting alerts for the cloud team.
- Azure Blueprints: A blueprint for new subscriptions related to role assignment, resources and policies.
- Role Based Access Control: Grant rights based on roles of employees and administrators.
- Privilege Identity Management: Being able to temporarily assign additional rights for management tasks.
Blog originally published in Dutch on the website of Microsoft Gold Partner 3fifty. If your are based in the Netherlands take a look at the website.
